
OpenAI’s Operator
OpenAI has recently unveiled Operator, a groundbreaking AI agent designed to transform how users interact with the web. Launched as a research preview on January 23, 2025, Operator represents a significant advancement in AI technology, allowing it to autonomously navigate the internet and perform various tasks that typically require human intervention.
At the core of Operator‘s functionality is the Computer-Using Agent (CUA) model, which integrates advanced vision capabilities with reasoning skills. Unlike traditional AI systems that rely on APIs, Operator simplifies user engagement by directly manipulating web interfaces, making it accessible even to those without technical expertise.
OpenAI’s iterative approach ensures that Operator will evolve based on user feedback, paving the way for future expansions to other subscription tiers. As businesses and individuals increasingly seek automation solutions, Operator stands poised to redefine the landscape of digital task management, bridging the gap between complex technology and everyday usability.
Key Features
OpenAI’s Operator combines advanced AI technology with user-centric design to create a powerful tool for automating online tasks efficiently and safely. As it continues to evolve, Operator promises to redefine how individuals and businesses interact with digital platforms.
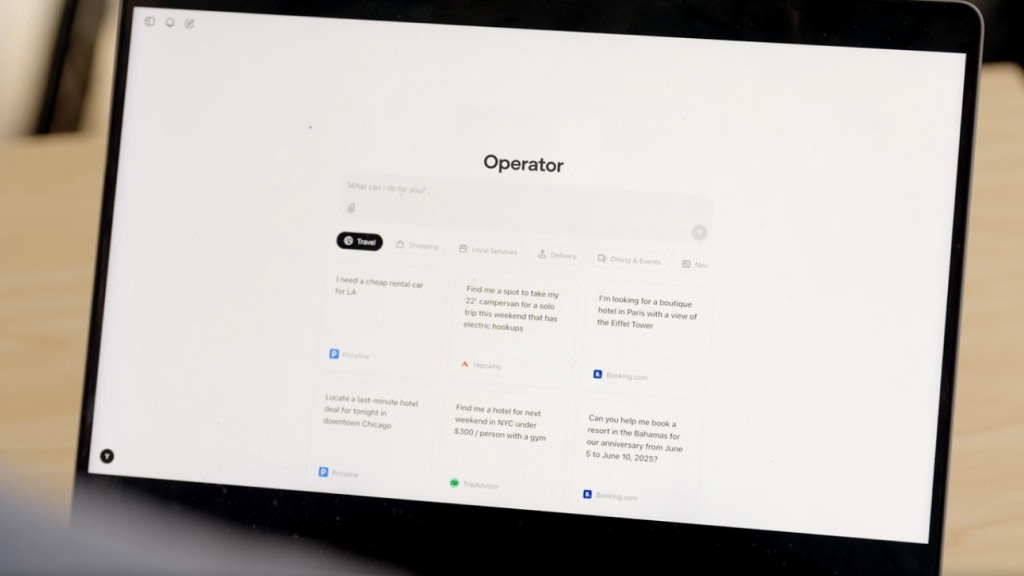
OpenAI’s Operator is currently available to ChatGPT Pro subscribers in the U.S., and is set to expand its reach to other user tiers in the future. Here are the key features that define Operator and how it operates:
1. Human-Like Browser Interaction
Operator mimics human behavior by controlling web browsers through keyboard typing and mouse clicking. This design eliminates the need for complex integrations or APIs, making it user-friendly and accessible to everyone, regardless of technical expertise.
2. Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
Powered by advanced reasoning capabilities, Operator breaks down tasks into manageable steps. It creates a list of actions to complete a task, allowing users to follow its progress in real-time. This structured approach enhances accuracy and adaptability in task execution.
3. Clarifying Questions
When faced with ambiguity, Operator can ask clarifying questions to gather more information from users. This feature ensures that tasks are completed according to user specifications, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the AI agent.
4. Versatility Across Websites
Operator is not limited to specific platforms; it can navigate and interact with virtually any website. This versatility allows it to perform a wide range of tasks, from booking travel arrangements to ordering groceries, making it a powerful tool for everyday use.
5. Safety and User Control
For sensitive actions, such as logging into accounts or making purchases, Operator hands control back to the user. This feature promotes safety and trust in its operations, ensuring users have the final say in critical transactions.
6. Real-Time Task Tracking
Users can monitor Operator‘s actions as they happen on the screen, providing transparency and allowing for adjustments if necessary. This real-time feedback loop enhances user engagement and confidence in the AI’s capabilities.
7. No Technical Expertise Required
With its intuitive interface, Operator requires no coding or technical knowledge, making it accessible for everyone. Users can simply type commands to initiate tasks, streamlining their online activities without needing specialized skills.
CUA – The Technology Behind Operator

The Computer-Using Agent (CUA) is the innovative technology powering OpenAI’s Operator, designed to revolutionize how users interact with digital environments. CUA combines the advanced vision capabilities of the GPT-4o model with sophisticated reasoning through reinforcement learning, enabling it to navigate and manipulate graphical user interfaces (GUIs) much like a human would.
At its core, CUA operates by taking screenshots of a web page, allowing it to analyze the visual elements such as buttons, menus, and text fields. This visual understanding enables the agent to perform tasks autonomously, executing actions like clicking and typing without relying on specific application programming interfaces (APIs). Instead of being limited to compatible sites, CUA can interact with virtually any web page, broadening its usability.
CUA employs a structured approach to task execution by breaking down complex actions into manageable steps and adapting when challenges arise. It utilizes a “chain-of-thought” reasoning process, which allows it to self-correct and backtrack if it encounters obstacles.
This groundbreaking technology marks a significant advancement in AI capabilities, paving the way for more intuitive and efficient digital interactions. As CUA continues to evolve, it holds promise for a wide range of applications across various industries.
Operator vs. Competitors

OpenAI’s Operator stands out in the competitive landscape of AI agents, particularly against offerings from Microsoft, Google, and Slack. Unlike these established players, Operator is designed to autonomously navigate the web and perform tasks without relying on APIs, which often limit functionality.
- Operator excels in browser task performance, achieving an impressive score of 87% on the WebVoyager benchmark, compared to Claude’s 56%. This superior performance highlights Operator’s efficiency in automating online tasks such as booking tickets and ordering groceries.
- Operator operates on a remote browser hosted on OpenAI servers, allowing it to handle multiple tasks simultaneously. In contrast, Claude can interact with both web and desktop applications but is often slower and more error-prone.
- Operator features robust self-correction mechanisms that allow it to adapt and seek user input when faced with challenges, ensuring greater reliability. While Operator is currently limited to Pro users at a subscription cost of $200 per month, Claude offers broader beta access for free.
- Microsoft’s AI agents, such as Copilot, focus on enhancing productivity within their suite of applications but do not offer the same level of independent web interaction. Similarly, Google’s Project Mariner utilizes its Gemini 2.0 model for automated tasks but lacks the universal interface that Operator provides, which enables it to work across any web platform.
- Slack’s AI tools primarily enhance communication and collaboration within its platform rather than performing diverse online tasks. On the other hand, Operator’s focus on browser automation and superior task execution positions it as a leading choice for users seeking efficient AI-driven solutions.
Overall, Operator‘s unique ability to function as a comprehensive task manager positions it as a formidable contender in the evolving AI landscape, offering users a seamless and efficient digital experience.
Tasks That Operator Can Perform Autonomously

OpenAI’s Operator is designed to autonomously perform a wide range of web-based tasks, significantly enhancing user productivity. Some of the specific tasks Operator can handle include:
-
Filling Out Forms
Operator can automatically complete online forms, saving users time on repetitive data entry.
-
Booking Reservations
Whether it’s securing a table at a restaurant or arranging travel accommodations, Operator can navigate booking websites and finalize reservations.
-
Shopping Online
Users can delegate shopping tasks to Operator, which can browse products, add items to the cart, and complete purchases.
-
Ordering Groceries
Operator simplifies grocery shopping by allowing users to specify items, which it then orders from various online retailers.
-
Researching Information
The AI agent can autonomously gather information from the web, making it useful for research tasks or finding specific details.
-
Creating Memes
Operator can also engage in creative tasks like meme generation, showcasing its versatility beyond traditional task automation.
OpenAI’s Operator is also designed to handle unexpected changes during tasks with remarkable adaptability. When faced with challenges, such as a complex interface or a CAPTCHA, Operator pauses its operations and notifies the user, allowing them to intervene. This collaborative approach ensures that users remain in control while the AI agent navigates various online environments.
Operator employs the chain-of-thought reasoning process, enabling it to backtrack and attempt alternative methods if it encounters obstacles. For instance, if a website’s layout changes unexpectedly, Operator can adjust its actions dynamically to continue the task. Additionally, it learns from these interactions through reinforcement learning, improving its performance over time.
This flexibility allows Operator to manage diverse tasks effectively, ensuring a seamless user experience even when faced with unforeseen circumstances. As it evolves, OpenAI aims to enhance Operator‘s error recovery mechanisms further, solidifying its role as a reliable digital assistant.
How Will Operator Integrate With ChatGPT in the Future?
Operator is currently only accessible to customers in the United States who have purchased OpenAI’s Pro membership. OpenAI stated that it intends to extend Operator to additional subscription plans, nations, and eventually the free version of ChatGPT. By doing this, OpenAI plans to enhance the user experience by seamlessly combining conversational AI with task automation. This integration will allow users to switch effortlessly between chatting with the AI and delegating tasks to Operator, creating a more cohesive interaction.
As part of this integration, Operator‘s capabilities will be made accessible to a broader audience, including users on the Plus, Team, and Enterprise subscription tiers. This expansion aims to democratize access to advanced AI functionalities, ensuring that more users can benefit from its ability to navigate the web and perform tasks autonomously.
Additionally, OpenAI is focused on refining Operator based on user feedback gathered during its initial rollout. This iterative approach will help improve its performance, and enhance its adaptability in handling complex interfaces.
Safeguards for Data Privacy

OpenAI’s Operator incorporates several robust safeguards to protect user data privacy while interacting with the web. Key measures include:
-
User Confirmation
Operator prompts users for confirmation before executing sensitive actions, such as submitting orders or sending emails. This allows users to review and approve actions before they are finalized, ensuring greater control over their data.
-
Takeover Mode
When sensitive information such as passwords or payment details needs to be entered, Operator activates “takeover mode.” In this mode, it halts screenshot collection, allowing users to input their information securely without the risk of exposure.
-
Website Restrictions
Operator is programmed to avoid certain categories of websites, such as gambling or adult content, minimizing the risk of misuse.
-
Real-Time Monitoring
The system employs real-time moderation to detect and prevent prompt injections or suspicious activities, pausing operations if necessary.
-
Data Management Options
Users can opt out of data collection for model training and delete browsing history and past conversations easily, enhancing user control over personal data.
These features collectively ensure that while Operator performs tasks autonomously, user privacy remains a top priority throughout its operations.














